In our laboratory, staff, graduate students, and undergraduate students are promoting research with the motto ”practice of health promotion science that leads to extension of healthy life expectancy". We believe that research should be able to contribute to the direction in which people and society can be happier and the staff will instruct students to carry out research with such a research mindset. We are doing!!!
The main research contents are as shown in the figure below (Fig. 1)

The specific research contents are introduced below.
Good management of lifestyle-related diseases is known to extend healthy life expectancy. In our laboratory, we are focusing on hypertension, which has the largest number of patients, establishes of guidance methods for lifestyle-related improvement by nurses and public health nurses often perform, proposals for more efficient methods, and patients who also consider genetic predisposition. We are researching intending to establish tailor-made treatments that appropriate for individuals.
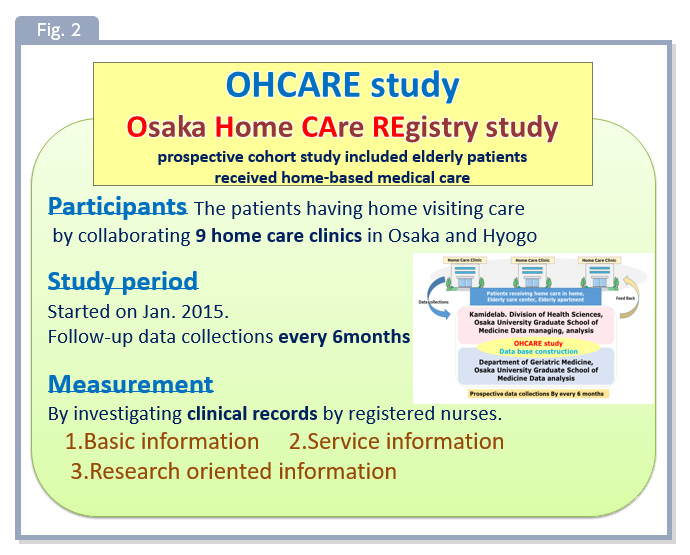
In the future, the aging rate will rise dramatically, the focus of medical care will shift from hospitals to homes. There is a lack of scientific evidence to provide more systematic, efficient, and satisfying home care for patients and caregivers. In our laboratory, we conducted Osaka Home Care Registry (OHCARE) research to establish comprehensive home medical care (Fig. 2). We investigate various issues such as disease management, nutrition, physical function, cognitive function, and care at home. We collect information and examine the related factors by quantitative analysis and hope to contribute to the construction of evidence to lead to problem-solving in- home medical care.
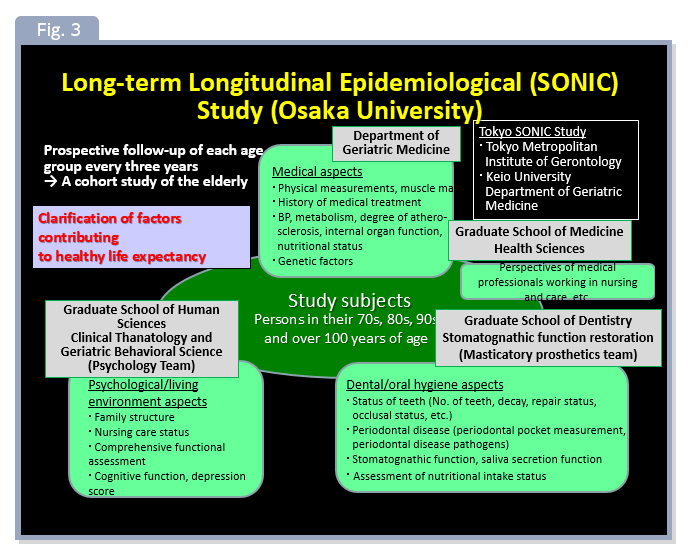
As the aging rate rising, the proportion of older people who need long-term care is steadily increasing. However, since the cost of long-term care insurance is limited, a society is desired in which the number of healthy older people who are independent without receiving long-term care is increasing as much as possible. For reaching this purpose, it is urgent to establish a long-term care prevention system. In our laboratory, we practice an attempt to clarify the factors of healthy longevity from multiple perspectives such as medicine, dentistry, and psychology through longitudinal epidemiological studies on older people (healthy longevity: SONIC study), as shown in Fig 3. We believe that the practice of health and longevity factors clarified here can be a goal for establishing long-term care prevention methods.
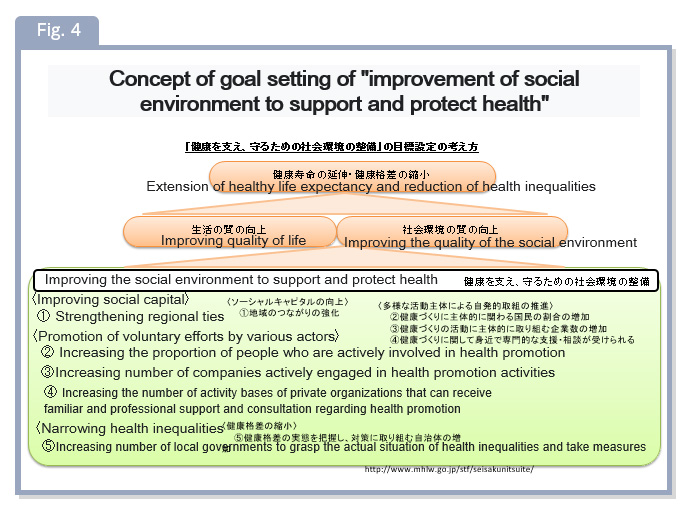
Communities (regions and belonging groups) that can trust the people around them and have a mutually beneficial relationship (reciprocity) are more comfortable to live in and work in, and communities with active participation are needed. It has become clear that we can take action to solve problems. It is called "Social Capital (SC)" including trust, mutual aid, and community participation. In recent years, research results suggesting that SC protects people's health in the community and global-wide, and it is attracting attention in the field of public health. In our laboratory, each activity, such as community and hobby activity, which is a social activity of people, are related to various indicators related to trust and reciprocity, SC, and individual health components. We aim to clarify the existence and contribute to promoting healthier community development in Japan, where the population is aging rapidly (Fig. 4).
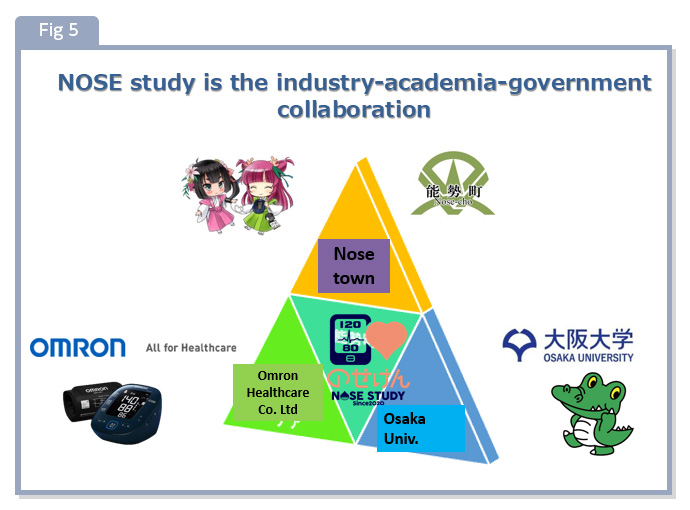
Blood pressure control is considered important for controlling the onset and progression of cerebrovascular disease, dementia, and geriatric syndrome, which are the causes of certification for long-term care. Recently, self-blood pressure measurement at home has been attracting attention. However, few studies have dealt with home blood pressure measurement and healthy life expectancy extension in the local community. Therefore, in our laboratory, we decided to conduct "Nose Town Health and Longevity Research" (Fig. 5) as industry-academia-government joint research with Nose Town, Toyono District, Osaka Prefecture, and OMRON HEALTHCARE. For people over 40 years old in Nose Town, we will verify whether self-measurement of blood pressure at home can prevent the onset of dementia, stroke and cardiovascular disease, geriatric syndrome, etc., and extend healthy life expectancy throughout Nose Town. This research is one of the five studies in the world adopted by OMRON HEALTHCARE's research grant Top-Z program. This study was the only one selected in Japan, and it is a global study that can bring new developments to blood pressure research. (Five adopted countries: Japan (Nose Town), Italy, Belgium, China, Taiwan)